Bone Grafting
Successful dental implants depend on having enough strong and healthy bone to support them. The jawbone provides the foundation for implants, ensuring they remain stable and functional for years to come. However, when teeth are lost, the bone in that area can shrink over time due to lack of stimulation. If there is not enough bone present, placing an implant can become difficult or even impossible without additional procedures. This is where bone grafting plays a crucial role in restoring lost bone and making dental implants possible. Bone grafting is a procedure used to regenerate lost bone, making it possible to place dental implants securely. If you have experienced bone loss due to missing teeth, injury, or gum disease, a bone graft may be necessary before or during implant placement.
1. Before Implant Placement:
This is done when there is extensive bone loss - including bone height and/or width, allowing bone to heal and form prior to the implant procedure.
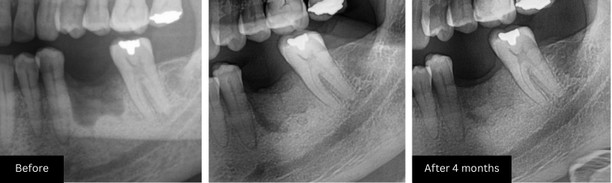
In the first X-ray, you can see significant bone loss at the lower left first molar area. The dark, hollow space shows that the ridge is too thin to support an implant. After the bone graft procedure, the follow-up X-ray shows new bone formation—the area now appears denser and more filled in, indicating healthy bone growth. This site is now ready for implant placement.
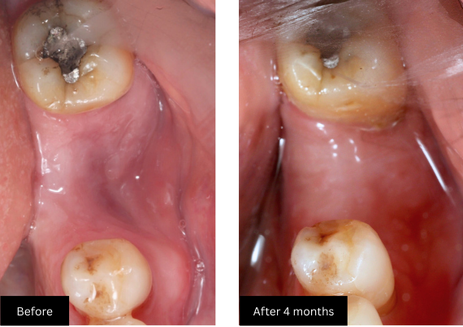
In the initial photo, you can clearly see the bone loss in width—the ridge has collapsed inward, and placing an implant would result in poor bone coverage and long-term instability. After bone grafting, the follow-up image shows a well-contoured ridge with adequate bone volume and healthy soft tissue. The area is now well-prepared for implant placement, with strong support and improved gum health.
2. Same time as Implant Placement:
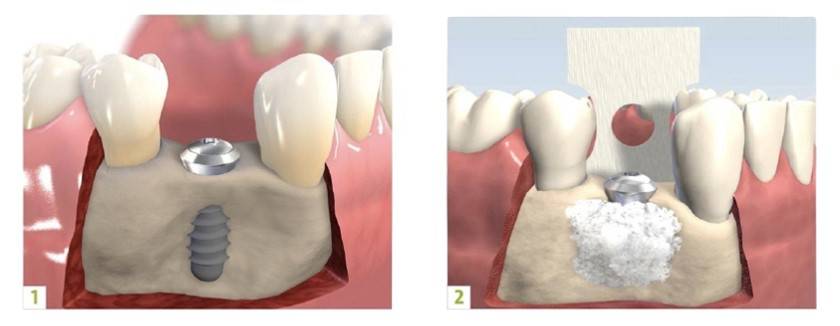
Bone Graft at the same time as implant placement
Sinus lifting
The maxillary sinus is an air-filled cavity located above the upper back teeth. When teeth in this area are lost, the sinus tends to droop or sag, reducing the amount of bone height available for implant placement. The longer the area remains untreated, the more bone loss occurs, making it difficult to place implants.
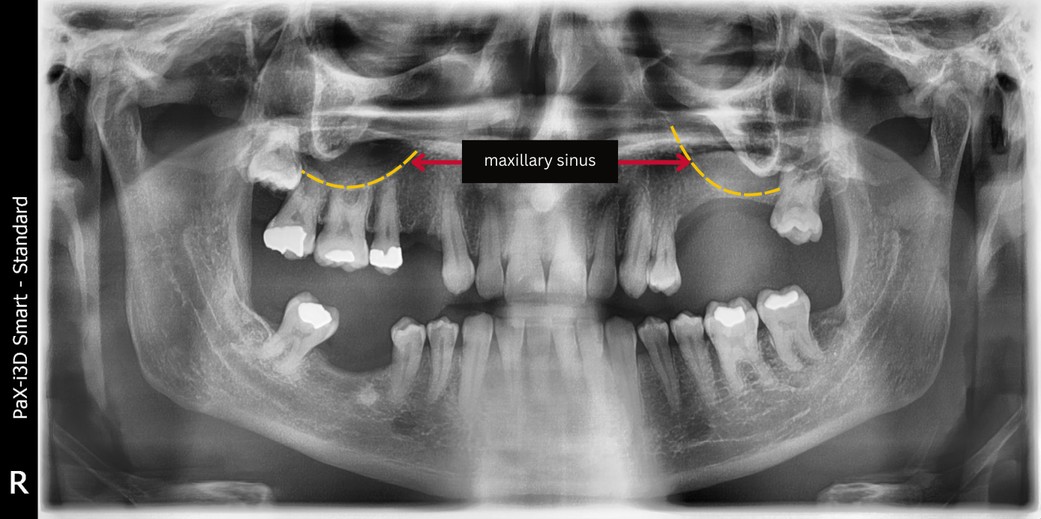
At SmileBox, we evaluate bone height using a CT scan to determine whether a sinus lift is necessary. An average implant length is 8-10mm, so 10-12mm bone is always required for implant placement. If bone height becomes less, the sinus lift procedure is done to achieve more bone height prior to implant placement. There are 2 techniques used depending on remaining bone height.
1. Closed Sinus Lift:
- Minimally invasive technique and used when there is already good bone height but an additional 1-4mm of bone is needed to support the implant.
- The sinus is gently lifted through the implant site, and bone graft material may be added to create the necessary bone volume.
- Implants are often be placed simultaneously, reducing overall treatment time.
- Treatment price is 15,000 THB - 35,000 THB
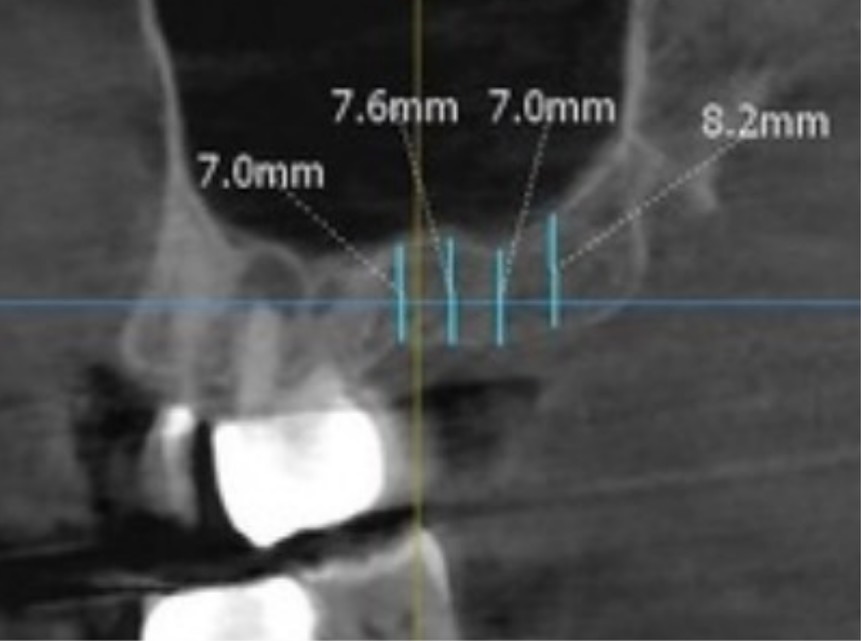
CT scan shows 7.0-7.6mm of bone height at implant site. Since an average of 8mm implant length will be used, only 1-3mm of sinus lifting is required. Therefore, the closed sinus lift technique can be used.
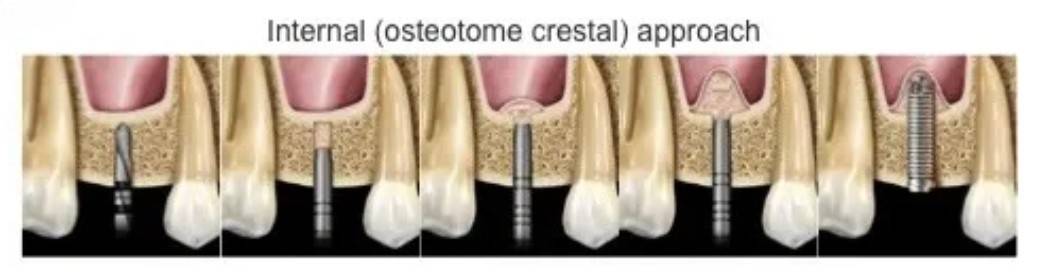
1. Osteotome Technique – A specialized instrument is used to carefully elevate the sinus floor while placing the bone graft
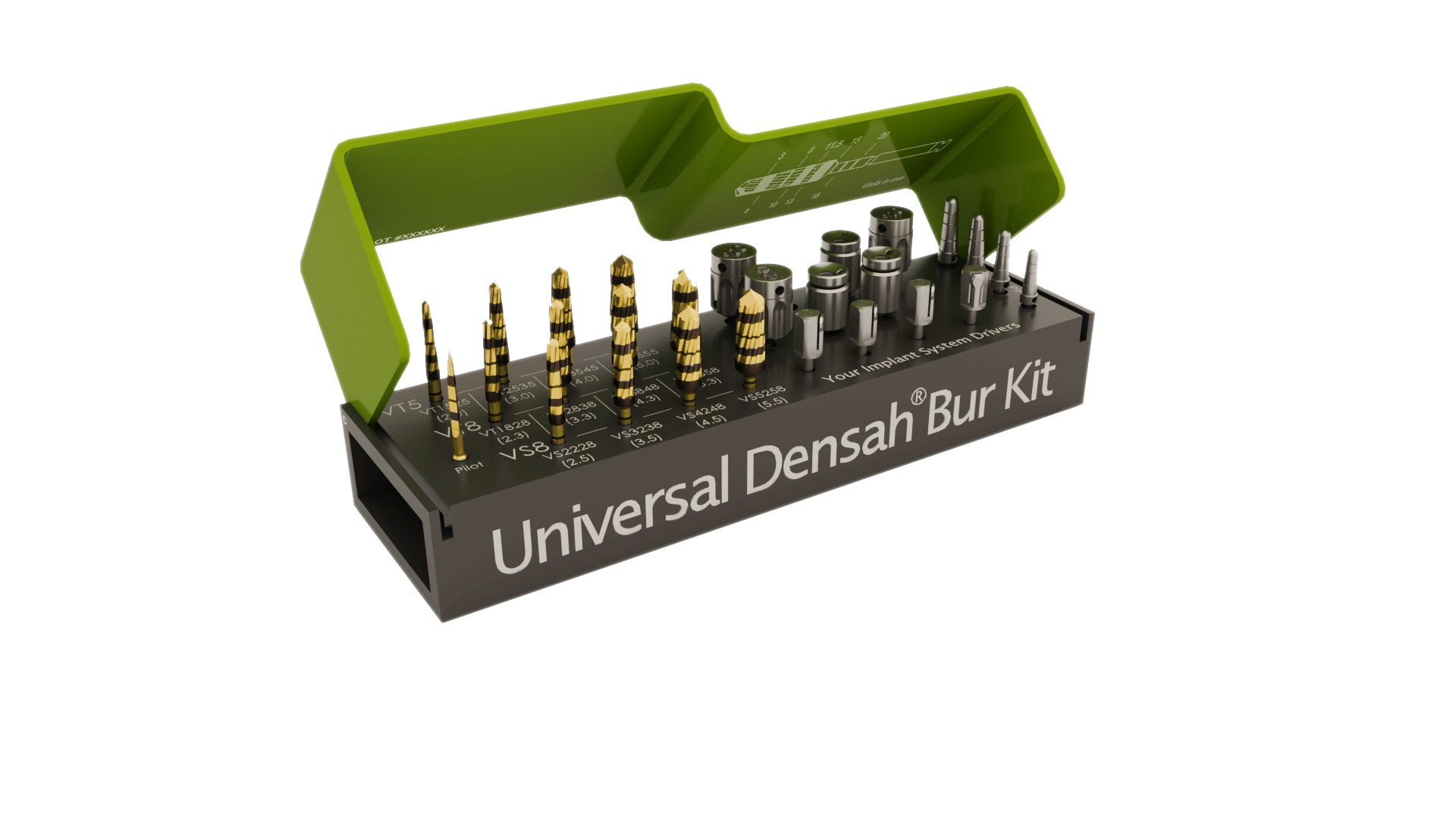
2. Osseodensification Using Densah Burs – A more advanced technique that preserves bone while simultaneously compacting and expanding it for improved stability. With osseodensitifcation, bone grafting is not required.

At SmileBox Implant & Cosmetic Center, our experienced doctors are highly skilled in performing both techniques, ensuring precision and successful outcomes for our patients.
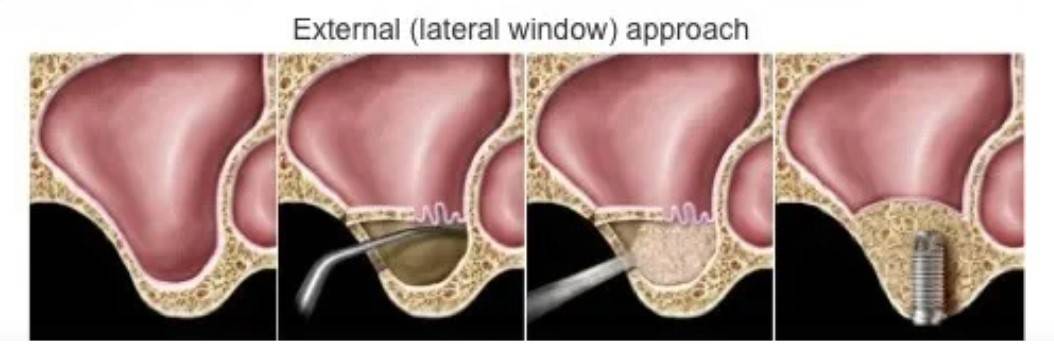
2. Open Sinus Lift:
- Done when more than 4mm of additional bone height is needed
- Involves making a small opening on the side of the upper jaw, lifting the sinus membrane, and placing bone graft material in the space.
- Implant placement may be done immediately or after healing, depending on factors like sinus physiology, bone quality, and the type of graft material used.
- Healing time for open sinus lift can be anywhere between 4-12 months.
- Treatment price is 35,000-50,000 THB
CT scan shows 1.0-1.8mm of bone height at implant site. Since an average of 8mm implant length will be used, up to 7-8mm of sinus lifting is required and the closed technique is not recommended. In this case, the doctor lifted the sinus using the lateral window or open technique.

If you’ve been told you need a bone graft or sinus lift before getting dental implants, our expert team at SmileBox Implant & Cosmetic Center is here to help. Contact us today for a consultation and let’s create a strong foundation for your new smile!
Book an Appointment Now
You can simply email your inquiry along with a few clear photos of your
teeth to [email protected].
Our Dental Consultants will get back to you as soon as possible.
If you need immediate assistance, please call us directly at
(+66)2-402-9542,
or reach out to us on Whatsapp at
(+66)63-352-3691.
We’re here to make you smile again.